
Published Research Resources


Black and White older adults’ end-of-life experiences: Does hospice use mitigate racial disparities?
Hospice use is associated with increased perceived death quality, particularly for Black decedents, suggesting that expanding equitable access to high-quality hospice services may be a promising pathway for intervention.




Residents living in areas where property remediation addressed both vacant lots and abandoned homes experienced significant increases in sense of community.

Green space goes hand-in-hand with cardiovascular health, with tree planting as a possible strategy to improve health. Research shows that areas with more plants and trees (greenness) are associated with lower incidence of cardiovascular disease.

Centering the needs of pregnant people and their families' and forming equitable collaborations between community and institutional partners can meaningfully transform care delivery systems and comprehensively meet the needs of the entire community.

US Army and Navy service members went to fewer therapy sessions during pregnancy and while on leave following birth, especially if they had already received mental health treatment before. Birthing parents were more likely to go back to therapy once they started working again.

The research team discovered that living in greener, more walkable neighborhoods is associated with lower incidence of Alzheimer's Disease.

The project team found that school-based mental health services increased average outpatient mental health service use and reduced self-reported suicide attempts.

The project team found that cash transfers on their were associated with increases in healthy behaviors and that the cash transfer paired with after-school programming was associated with an improvement in the financial health of participants.








This paper introduces the COVID-19 US State Policy (CUSP) Database, a continuously updated repository of policies, as well as highlights how the research conducted using the database has impacted policy decisions.



The TROLLEY (TRansit Opportunities for HeaLth, Livability, Exercise and EquitY) study will use rigorous methods, as described in this Study Protocol paper in BMC Public Health, to advance our understanding of health, well-being, and equity-oriented outcomes of new light rail transit (LRT) li

When children are no longer eligible for the Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC) due to age requirements, mothers reduce their own nutritional intake to provide more food for their children.

Recent findings suggest that with later start times, students obtain more sleep, and in turn have improved attention and vigilance, which are critical for new drivers.

Birthing parents need parental leave to physically recover from birth, in addition to any benefits of bonding and caring for the baby.

Supportive prenatal substance use policies that created/funded targeted substance use disorder treatment programs led to reductions in opioid overdoses and increases in the use of opioid use disorder medications for pregnant people.

Policies criminalizing maternal substance use or classifying it as child maltreatment are associated with an 18.9% increase in infant maltreatment reports, which may lead to a fear of experiencing child protective services involvement and reduced chances of reunificat


Supportive prenatal substance use policies are those in which pregnant people are provided access to treatment or other support programs. Such policies lead to better outcomes for babies: preterm births and low birth weight births both decreased by 2%.


Growing evidence indicates that policy around policing needs to focus on the relationship between frequent police interactions and health and violence outcomes.


Supplementing with K-12 student education with programs, such as those developed by Generation Citizen, that encourage community and civic engagement in a non-partisan way can provide students with "a local focus, inclusive, diverse learning environments, and access to communities."

Students exposed to The Bigger Picture curriculum were more likely to identify that diabetes is not just an individual problem, but a structural problem with environmental, historical, political, and sociocultural roots.


Findings from the Lanham Preschool Study suggest that investments in universal, widely accessible child-care can be beneficial, but that design and implementation need to be scrutinized to ensure the benefits are accrued equitably.

This study evaluates multiple factors associated with Tobacco 21 (T21) policy adoption in the U.S. from 2015 to 2019 before the nationwide adoption of T21 to identify disparities between regions that adopted the policy and those that did not.



Exploring the impacts of various types of messaging (narratives, simple propolicy, and a combination of the two), the authors found that messages could backfire and inadvertently lead to a diminished support from state legislators.
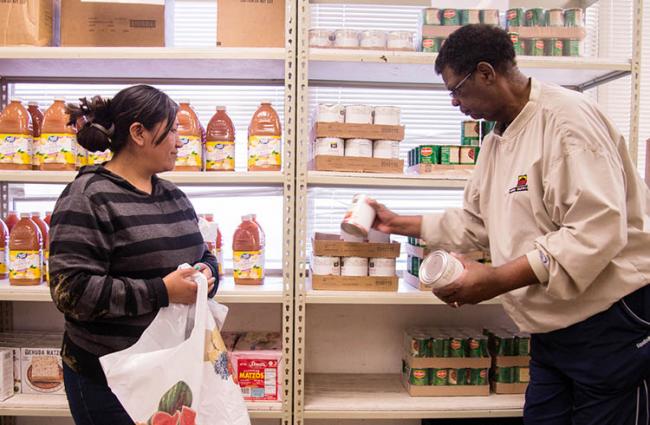


Impact of changes in the frequency of food pantry utilization on client food security and well‐being
When clients receive food assistance one month and then skip the following month, some might assume that this is because the food assistance has fulfilled its intended mission and that the household who did not show up to receive food is no longer in need of emergency assistance.

Shifting school start times to 8:30 am or later for middle/high school students is a critical health policy that can quickly and effectively address significant adolescent sleep debt, with minimal impact on younger students, who often are required to start earlier in order to accommodate later se

Weatherization improves self-reported health and saves families money.

Weatherization programs could be improved by expanding eligibility for inclusion beyond income and by collaborating with the healthcare and public health sectors to identify those households most in need of their services.

Community collective efficacy, or a community’s ability to mobilize and realize shared goals, has been linked to positive health outcomes, lower crime and violence, and residents’ emotional connection to their community.

Unemployment insurance reduced food insecurity for those individuals that lost employment during the COVID-19 pandemic. The $600 weekly supplement was associated with further declines in food insecurity.
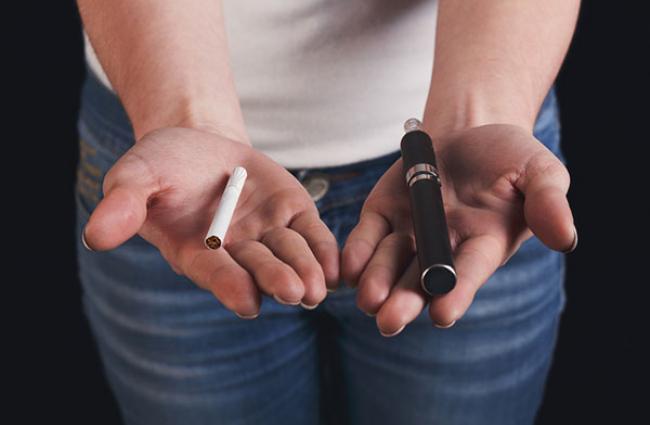

Smoke-free worksite laws lead to reductions in current smoking, increases in smoking cessation, and decreases in recent vaping. However, adding vaping restrictions to these laws may have actually reduced the impact of the law on current smoking among 18 to 25 year-olds.






Extending prenatal care to low-income, immigrant women, regardless of citizenship status, is a cost-effective and life-saving strategy.

Access to 2-year post-high school institutions positively impacts schooling attainment, as well as subsequent employment and earning levels. This is particularly evident for whites and Hispanics.

Place-based interventions have the potential to improve the health and safety of communities experience disadvantage.


Interventions targeting parental incarceration and involvement with the criminal justice system could have far-reaching health, wellbeing, and equity impacts for parents and children.


Two policies—universal background checks and “may issue” laws that required a heightened showing of suitability for concealed carry—were associated with lower firearm homicide rates in large cities but were not associated with firearm homicide rates in suburban and rural areas.

County- and municipality-level policies restricting tobacco sales to individuals younger than 21, so-called Tobacco 21 or T21 laws, led to substantial reductions in smoking in 18- to 20-year olds.


Supportive and flexible employment policies at early care and education centers could improve health and equity outcomes for teachers, such as providing meals to teachers, reducing teacher-to-child ratios, paid and sick leave policies, etc.


The Impact of State Firearm Laws on Homicide and Suicide Deaths in the USA, 1991–2016: A Panel Study





This paper proposes strategies for defining, identifying, and estimating features of treatment-effect distributions in contexts where multiple outcomes are of interest.




The authors discuss the downstream impacts on children of parental involvement with the criminal justice system.


A mother's eligibility for the Deferred Action for Childhood Arrivals (DACA) was associated with an increased likelihood that her child(ren) participated in the Women, Infants, and Children Program (WIC).













Background: Persons accessing food from nonprofit distribution sites face numerous challenges and typically have significant unmet health needs. However, given limited and intermittent healthcare system engagement, this vulnerable population is underrepresented in clinical research.